Instrument Takeoff, Climb, SIDs, and Arcing Procedures
UJPT, E2-C2, & IUT BIFP-01
Sg 4, fr 11
Sg 4, fr 12, p1
Sg 4, fr 12, p2
R270
R270
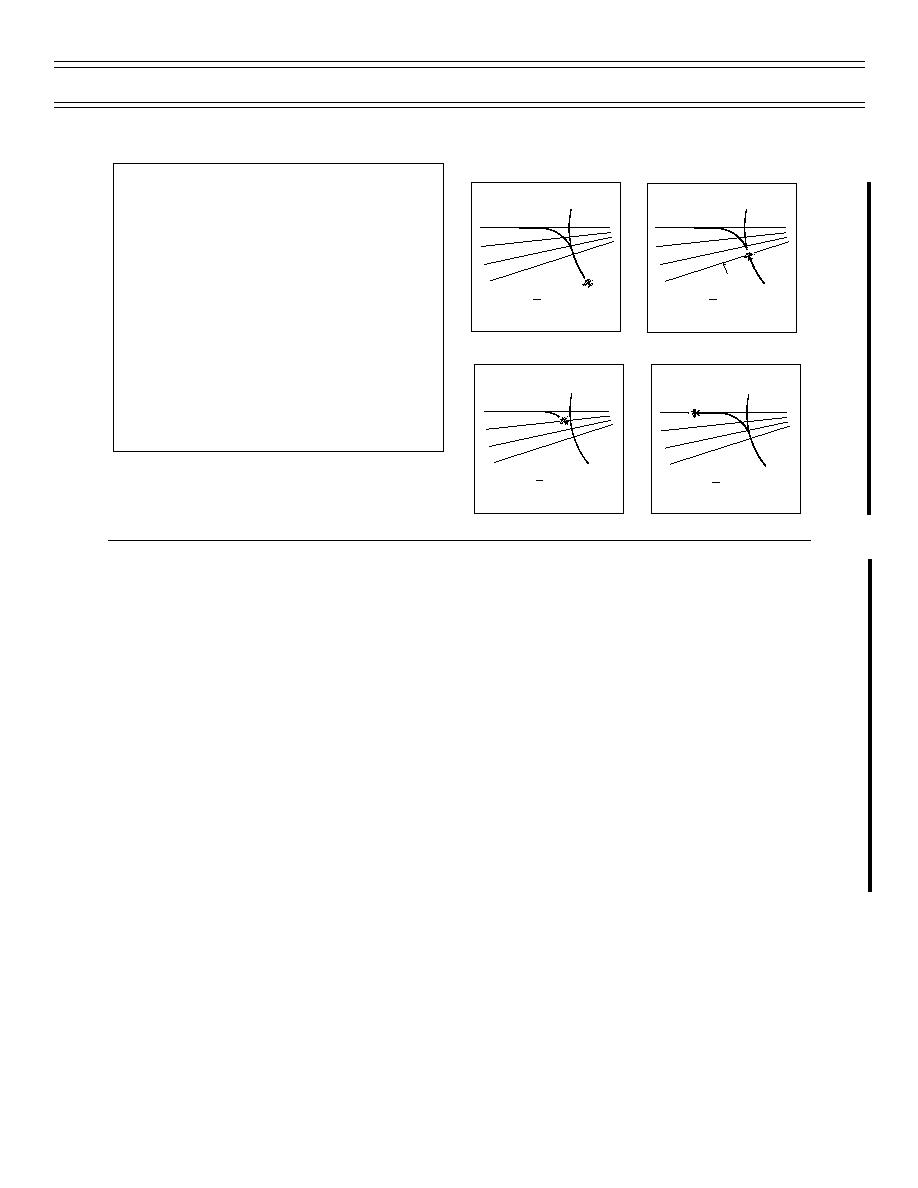
(60 / ARC DME) X 1% GS = NUMBER OF LEAD
R264
R264
RADIALS
R258
R258
10DMEARC
10DMEARC
R252
R252
18RadialLead
300KGS
300KGS
1/2SRT
1/2SRT
(USING 1/2 SRT)
60 X 1%GS=LeadRadial
60 X 1%GS=LeadRadial
DME
DME
ARC TO RADIAL INTERCEPTS
ARC TO RADIAL INTERCEPTS
Sg 4, fr 13
Sg 4, fr 12, p3
Vary AOB to intercept desired inbound/outbound radial
R270
R270
R264
R264
ARC TO RADIAL LEAD POINT CALCULATION
R258
R258
10DMEARC
10DMEARC
R252
R252
300KGS
300KGS
1/2SRT
1/2SRT
60 X 1%GS=LeadRadial
60 X 1%GS=LeadRadial
DME
DME
ARC TO RADIAL INTERCEPTS
ARC TO RADIAL INTERCEPTS
E.
Intercepting a radial from an arc 2.6.6.3
1.
Set desired course in course select window and determine direction of
turn
2.
Determine lead in radials
NOTE: Apply the following formula to determine lead radials: "(60/DME) x
1% ground speed = lead radials."
3.
At designated lead radial, begin 1/2 SRT
NOTE: Do not exceed 30 degrees AOB.
4.
During turn, vary AOB as required using the movement of the CDI to
intercept the outbound/inbound course on the radial
(03-97) Original
Page 1-15



 Previous Page
Previous Page
