T-45C TS, ADV & IUT FamFP-02
Familiarization Flight Procedures
4.
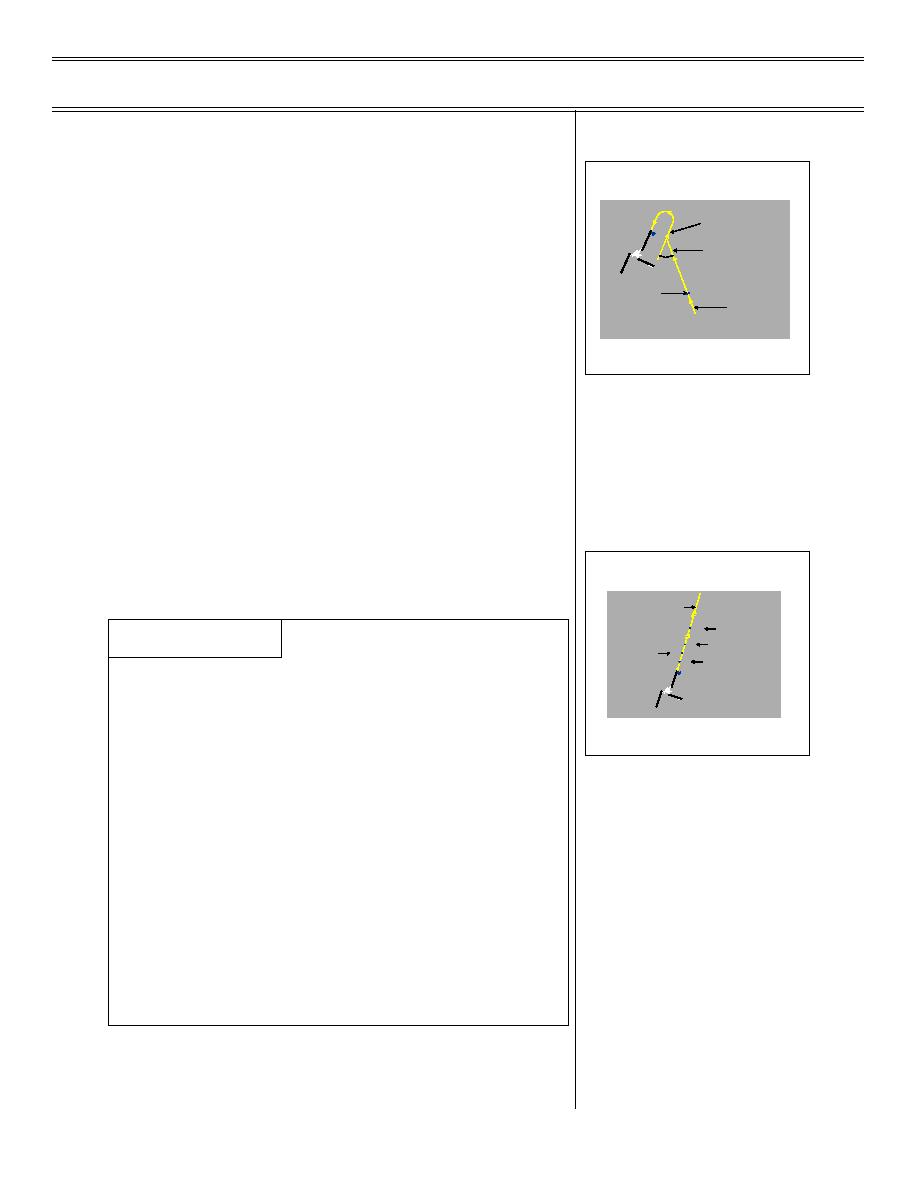
Establish downwind
Sg 2, fr 3
a.
Descend to and maintain 600 ft AGL
ESTABLISH DOWNWIND, DESCEND
TO PATTERN ALTITUDE (DIRTY)
NMM
CH56
LOWER LANDING GEAR AND
b.
Maintain optimum AOA
FLAPS, AS REQUIRED, PRIOR
TO DOWNWIND
45%
DESCEND TO 300 FT
5 NM
5.
Communicate (to request landing): "Tower,
ABOVE TRAFFIC
PATTERN
SLOW TO 200 KIAS
Bass one seven zero, abeam, three down
VFR DOWNWIND ENTRY
and locked, full-stop [or roll and go]"
VFR DOWNWIND ENTRY
6.
Maintain proper distance abeam the run-
way: approximately 1 nm laterally
7.
Fly normal pattern
NOTE: Watch for other aircraft in the break and
possible interval conflicts.
B. VFR straight-in approach
Sg 2, fr 4
REQUEST CLEARANCE
FROMTOWER
1,500 FT MSL
10NM
LECTURE NOTES
SLOW TO 200 KIAS
INITIAL
800 FT AGL
ON-SPEEDPOINT
3 NM
(DIRTY)
800 FEET AGL
2 NM
BEGIN DESCENT
400 FT AGL
NOLOWER THAN 300 FTAGL
1 NM
(UNTIL BALL ONOLS)
Clarify that VFR straight-in procedures may be locally
NMMCH56
customized to accommodate unique traffic deconfliction
VFR STRAIGHT-IN ENTRY
needs. When recovering at other bases via a VFR
VFR STRAIGHT-IN ENTRY
straight-in, pilots arriving IFR or using VFR flight-follow-
ing may be handed off to Tower by RAPCON at a
locally agreed to altitude that accomplishes a
deconfliction necessity. However, so long as an aircraft
contacts Tower on a VFR clearance, Tower will not
"assign" an altitude; that is the pilot's discretion, and
traffic avoidance is primarily his responsibility. As a
general rule, control tower personnel prefer to receive a
radio call requesting a VFR straight-in, no closer than
10 nm to the field. That minimum distance facilitates
this traffic sequencing responsibility.
Page 2-9
(9-99) Original



 Previous Page
Previous Page
