T-45A UJPT & E2-C2 INav-01
Review of FLIP and Publications
Enroute
High Altitude Charts
Application
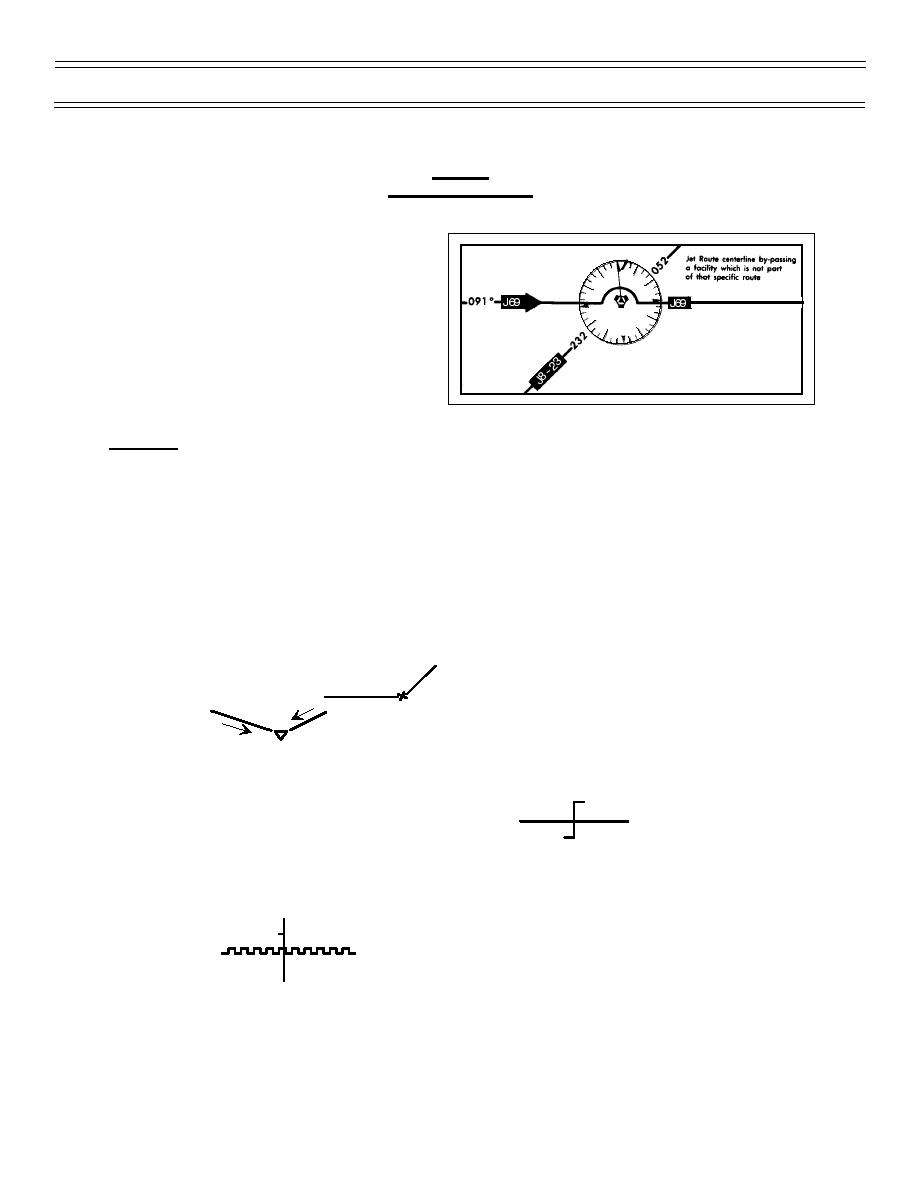
Jet routes, unlike low altitude airways, have no
defined width. Their centerlines terminate at the
outer edges of the NAVAID compass roses. A
jet route extending through a compass rose
around a NAVAID indicates the NAVAID is not
part of that jet route. It is not used for navigation
along the penetrating jet route and would not be
indicated in the route-of-flight section of your
flight plan unless you were filing “Direct” to that
NAVAID. For a NAVAID to be part of a jet route
segment, there must be a course depicted on
both sides of the compass rose, or the route terminates at the compass rose.
NOTE: The compass rose is oriented to magnetic north of the NAVAID which may not be adjusted to the
charted isogonic values.
To ensure all pilots fly the centerline of jet routes and achieve maximum navigational signal reception,
three types of definite changeover points (COPs) are prescribed by FAR Part 95 where pilots should
change VOR frequencies and/or TACAN channels and reset their course selectors to the inbound course
for the next NAVAID along each route segment.
1. On a relatively straight leg, change halfway, which is the point of equal signal strength; or,
2. Where the route takes a significant turn, change at the point of turn, which is the DME position
depicted by the symbol
or a dogleg at an intersection on the
chart
; or,
3. If the point of equal signal strength is not halfway, at the designated VORTAC changeover point
along the route depicted on the chart by the symbol
.
30
93
While proceeding on the enroute portion of your flight, you will be directed to change Air Route Traffic
Control Center (ARTCC) frequencies as you proceed from sector to sector and from Center to Center
areas of responsibility. The boundaries for ARTCC areas of control responsibility are depicted on charts
FORT WORTH
by the symbol:
.
HOUSTON
(6-99) Original
Page 1-28



 Previous Page
Previous Page
