Aero Chapter 01, General Aerodynamics Review
T-45 Aerodynamics Student Workbook
TOTAL DRAG
Adding parasite and induced drag forms a “U” shaped total drag curve with total drag at a minimum where
induced and parasite drag are equal (Figure 5). At the point where the total drag is at a minimum, the lift-
to-drag ratio will be maximum L/D or (L/D)max. The airspeed/AOA for maximum endurance, maximum
climb angle, and maximum power off glide range will be found at (L/D)max in turbojet or turbofan aircraft.
WAVE DRAG
Wave drag is similar to parasitic drag but only occurs in conditions of supersonic flow. A body generating
a shock wave feels this force as a consequence of pressure differences in the shock.
WEIGHT
Weight results from the action of gravity on an aircraft and is normally expressed in pounds. Weight
varies with fuel, ordnance load, and g-load. The weight vector, by definition, acts through the center of
gravity (CG).
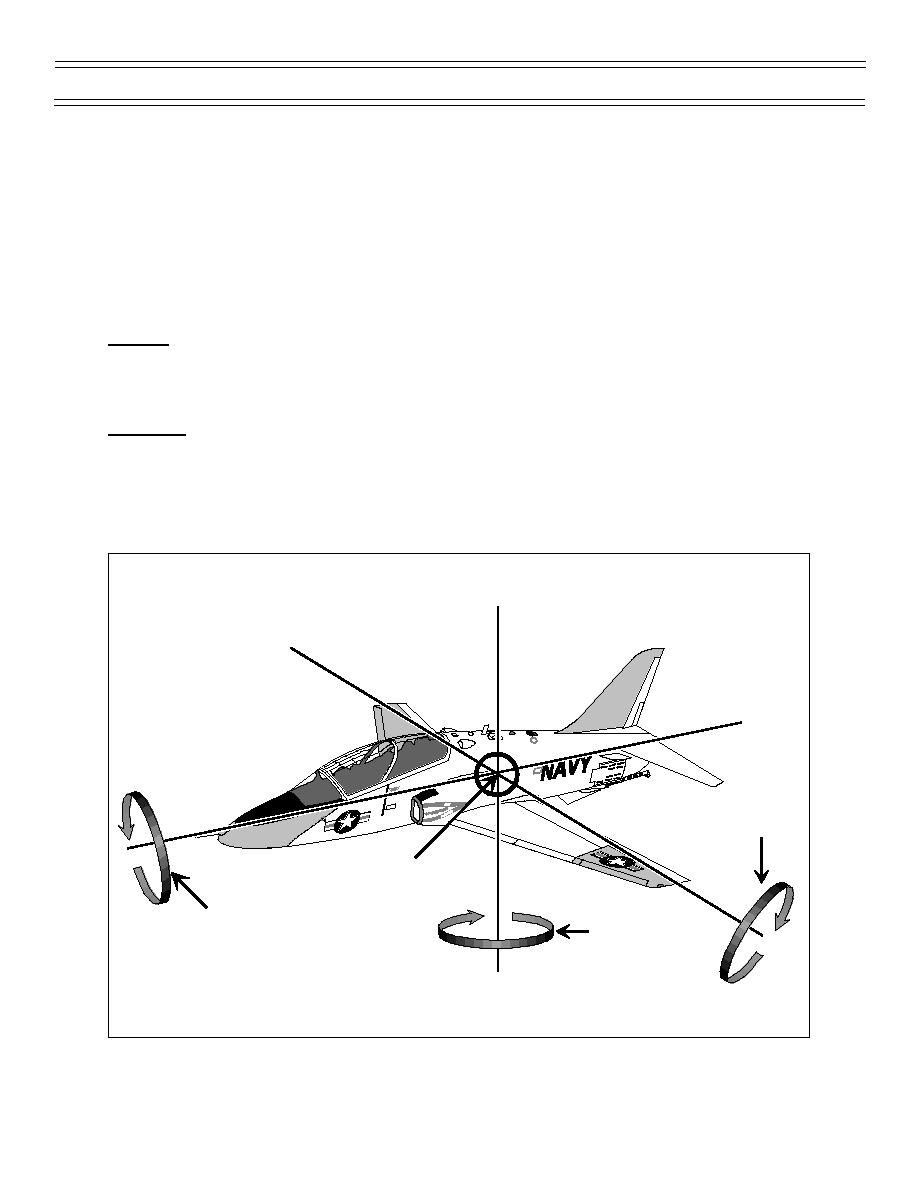
STABILITY
Stability refers to the tendency of an aircraft to resist displacement from its flight path and, if displaced, to
develop moments and forces to return to its original flight path. Stability is commonly represented as
movement about one of three axes of flight (Figure 6). Stability in roll is stability about the longitudinal
axis; stability in pitch is stability about the lateral axis; stability in yaw is stability about the vertical axis.
VERTICAL
AXIS
LATERAL
AXIS
LONGITUDINAL
AXIS
Pitch
CENTER OF
GRAVITY
Roll
Yaw
Figure 6: THREE AXES OF FLIGHT
Page 4
(7-99) Original



 Previous Page
Previous Page
