Aero Chapter 01, General Aerodynamics Review
T-45 Aerodynamics Student Workbook
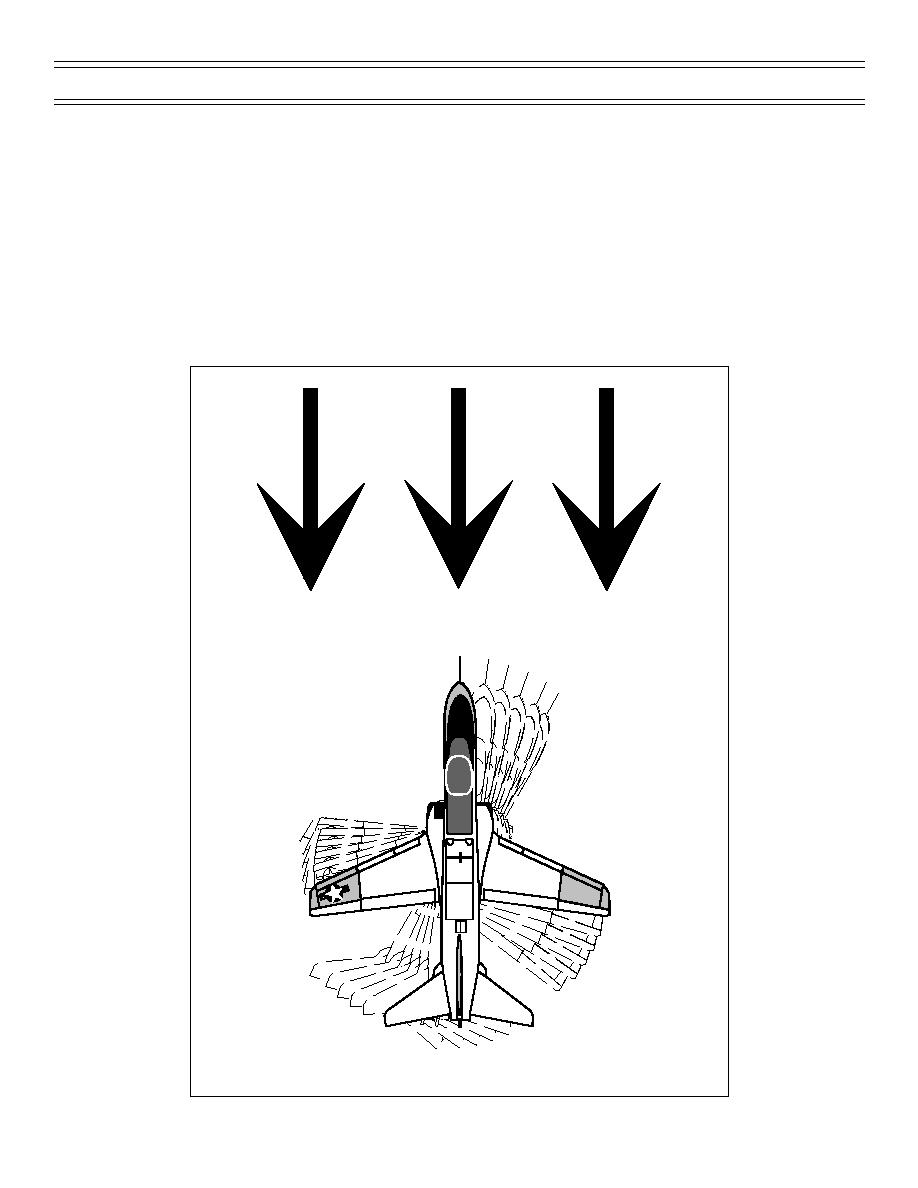
DIRECTIONAL STABILITY
Static directional stability or stability in yaw indicates an aircraft tendency to return to coordinated flight
when displaced by sideslip or skid (Figure 9).
Strong directional stability will be present in an aircraft that has a large sail area aft of the CG compared to
the area forward of the CG. With a yaw, the wind striking the area aft of CG will restore the nose into the
relative wind while the wind affecting the area forward of CG will attempt to continue the aircraft in the
yaw. The sideways lift created around the vertical stabilizer will have an additional effect on directional
stability. The vertical stabilizer will act as a wing and generate lift that acts horizontally, restoring the
aircraft in yaw.
Figure 9: DIRECTIONAL STABILITY
Page 7
(7-99) Original



 Previous Page
Previous Page
