 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 1-7. Risk categorization of food establishments |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
| 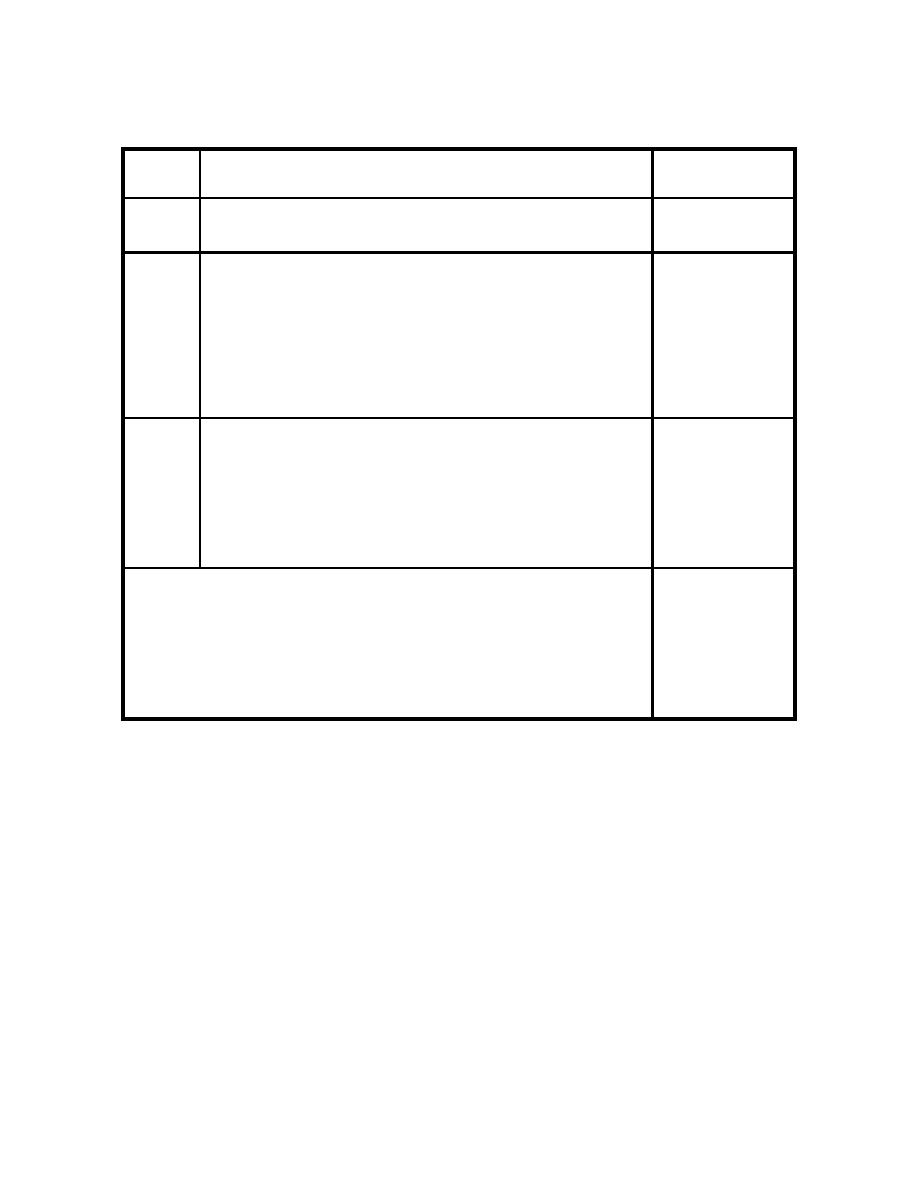 MANUAL OF NAVAL PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Table 1-7.
Risk categorization of food establishments
RISK
FACILITY
TYPE
RISK TYPE CATEGORY DESCRIPTION
TYPE
ARO's
1
Pre-packaged nonpotentially hazardous foods
only. Limited preparation of nonpotentially
hazardous foods only.
2
Limited menu (1 or 2 main items). Pre-packaged
raw ingredients are cooked or prepared to order.
Retail food operations exclude deli or seafood
HOT DOG
departments. Raw ingredients require minimal
TRAILER
assembly. Most products are cooked/prepared and
served immediately. Hot and cold holding of
SMALL DELI
potentially hazardous foods is restricted to
single meal service. Preparation processes
requiring cooking, cooling, and reheating are
limited to 1 or 2 potentially hazardous foods.
3
Extensive handling of raw ingredients.
Preparation process includes the cooking,
cooling, and reheating of potentially hazardous
foods. A variety of processes require hot and
LARGE DELI
cold holding of potentially hazardous food.
SMALL CLUB
Advance preparation for next day-service is
limited to 2 or 3 items. Retail food operations
include deli and seafood departments.
Establishments doing food processing at retail.
4
Extensive handling of raw ingredients.
Preparation processes include the cooking,
FULL SERVICE
cooling, and reheating of potentially hazardous
FACILITIES
foods. A variety of processes require hot and
cold holding of potentially hazardous foods.
(Shore
Food processes include advanced preparation for
galley's,
next-day service. Category would also include
ships and
those facilities whose primary service
submarines
population is immunocompromised.
galley's)
c. Previous compliance history should also be considered when
establishing inspection frequency. Non-conformance with critical Code
items or HACCP plan requirements may move an establishment up into more
frequent inspections until a record of more consistent compliance is
achieved.
d. There is a wide variety of methods for assigning establishments to
risk categories. The simplest method for that jurisdiction is often the
best.
e. Resources need to be allocated for seasonal and temporary food
establishment operations. Frequently, this involves scheduling inspections
on weekends and during evening hours.
f. It may be useful to schedule a number of inspections during the
evening hours to get a more balanced view of certain food operations.
118
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |