Instrument Failures and GPS/INS Failures
T-45C TS & ADV BIFP-09; IUT BIFP-05
VIII. Barometric altimeter failure
Sg 8, fr 2
INSTRUMENT FAILURES
A. Use ADI and HUD altitude
* GINA failure
* Standby attitude indicator
failure
*
MFD failure
* AOA indicator failure
B. Cross-check other pitot static system
*
HSI failure
* Radar altimeter failure
*
ADI failure
* VOR failure
instruments for correct operation
*
Turn and slip
* TACAN bearing/DME
indicator failure
failure
*
Pitot static
* ILS glideslope failure
malfunctions
C. If all barometric altitude information lost
*
Airspeed indicator * ILS localizer failure
failure
*
Barometric
* ILS marker beacon failure
altimeter failure
1.
Use radar altimeter for altitude information
*
Vertical speed
* Flight with partial panel
indication failure
or cross-check of barometric altitude below
5,000 ft AGL
Sg 8, fr 3
2.
Use cabin pressure above 5,000 ft AGL
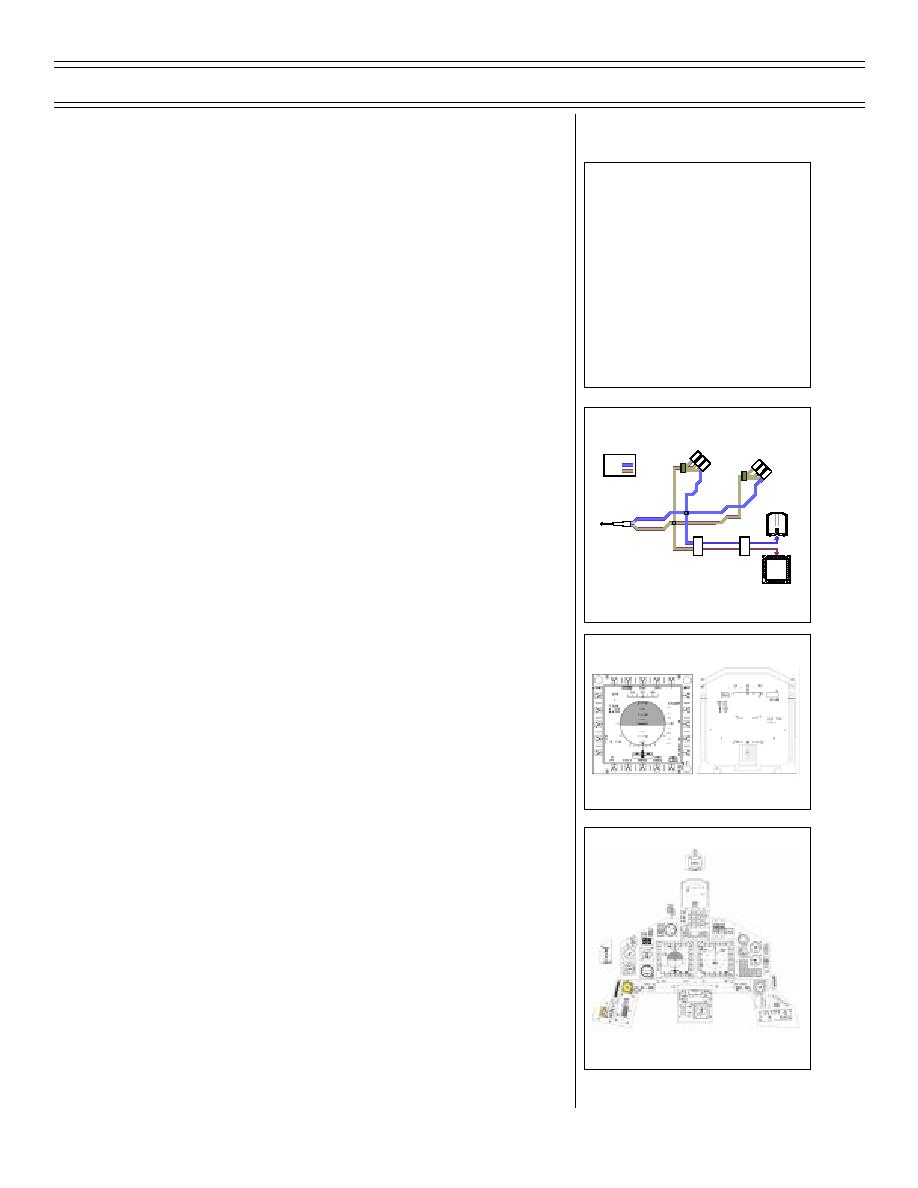
STANDBYALTIMETER
STANDBY
STANDBYVSI
FORWARD
ALTIMETER
COCKPIT
LEGEND
STANDBY
AIRSPEED
STANDBYVSI
PITOT
INDICATOR
STANDBY
STATIC
AIRSPEED
INDICATOR
a.
Cabin must be depressurized above
AFT
COCKPIT
5,000 ft MSL
HUD
ON
AIRSPEED
S
D
A
E
D
NOTE: Depressurized flight above
U
S
BAROMETRIC
ALTITUDE
MFD
25,000 ft MSL is prohibited.
D
N
N
OFF
OF
PITOT STATIC SYSTEM
b.
Accurate to +/- 500 ft
Sg 8, fr 4
D. Procedure for dealing with barometric altimeter
failure
1.
Check PITOT HEAT—ON
2.
Report altimeter failure to ATC
ADI AND HUD RADAR ALTITUDE
3.
Use the radar and the cabin pressure
altimeter for altitude
Sg 8, fr 5
4.
IFF-encoded altitude signal may also be in
error
5.
Land as soon as practicable
CABIN PRESSURE ALTIMETER
(4-01) Original
Page 9-17



 Previous Page
Previous Page
