 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  INTERCEPT PROCEDURES TEXTBOOK
Figure 5
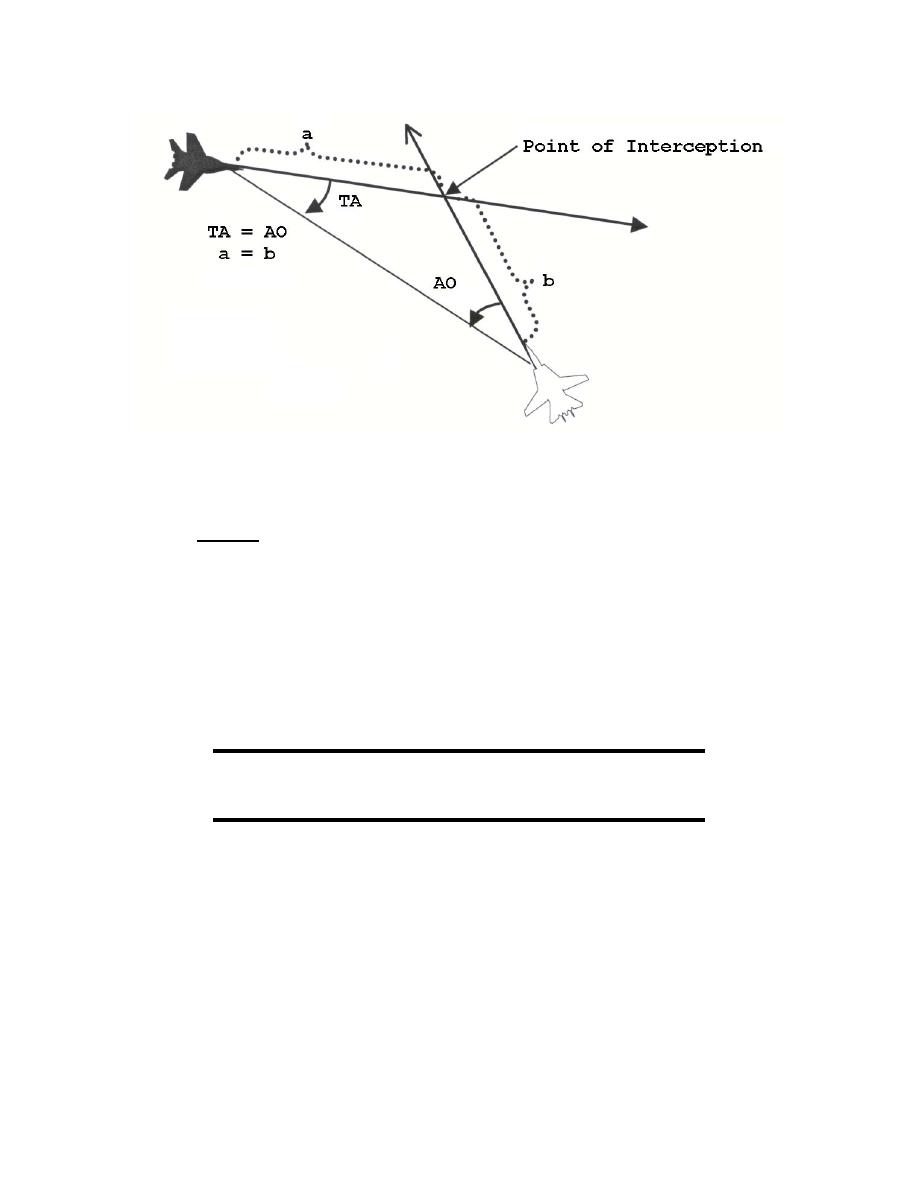
If the intercept triangle is an isosceles triangle with the above conditions established, TA
must equal AO in magnitude. However, in the above example, note that TA = AO in quantity
but they are opposite in direction. The fighter is right of the bogey's nose and the bogey is left of
the fighter's nose. Since both aircraft are the same distance from the point of impact and are
traveling at the same speed, TA will continue to equal AO in quantity as both aircraft approach
the point of impact.
Collision Course Definition
Knowing that TA will always equal AO when a collision intercept has been established in a
co-speed situation, the fighter can establish a collision intercept by adjusting the heading to
match the AO with the previously calculated TA.
When co-speed, a collision course is the fighter heading
that makes angle off equal in quantity, but
opposite in direction to target aspect.
In the following example, if given 20R TA, the fighter must turn left to yield 20L AO.
This would establish equal and opposite angles of an isosceles triangle or a collision intercept,
assuming a co-speed set-up.
46
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |