 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  AVIATION WEATHER
CHAPTER FIVE
RVR is the horizontal distance, expressed in hundreds of feet or meters, a pilot will see by
looking down the runway from the approach end. For takeoff and landing under IFR, prevailing
visibility is not as important as the visibility within the runway environment.
Surface vs Flight Visibility
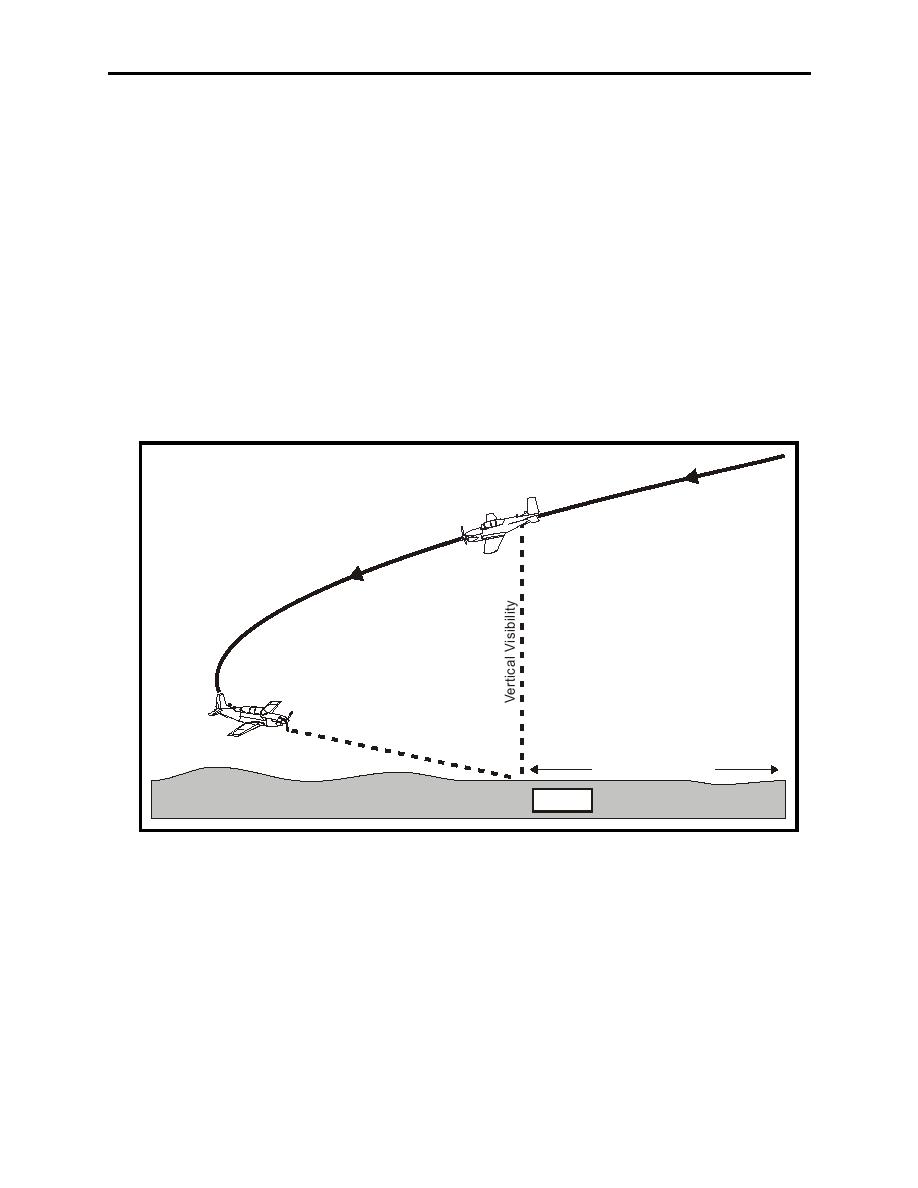
RVR and prevailing visibility are horizontal visibilities near the Earth's surface. They may be
quite different from the vertical visibility when looking down at the ground from an aircraft in
flight. For example, surface visibility may be seriously reduced by fog or blowing snow, yet only
a slight reduction in visibility is apparent when viewed from above the field. In Figure 5-15, the
airfield may be seen relatively clearly from above the fog. When descending to the level of the
fog, however, the airfield may disappear from sight. In another situation, flying into the setting
sun on a hazy day may reduce flight visibility to values less than the surface visibility. When
given the surface visibility, learn to anticipate what your flight visibility is likely to be. It may
vary, depending on other weather conditions present.
Slant R
ange V
is
ibility
Prevailing Visibility
1/2 Mile Due to Fog
Airfield
Figure 5-15 Surface vs Flight Visibility
Obscuring Phenomena
Obscuring phenomena are any collection of particles reducing horizontal visibility to less than
six miles. They may be either surface based or aloft. Examples include fog, haze, smoke,
volcanic ash, and blowing spray, to name a few.
Haze produces a bluish color when viewed against the ground. Although haze may occur at any
level in the troposphere, it is more common in the lower few thousand feet. Haze is associated
Weather Hazards of Turbulence, Icing, Ceilings, Visibility, and Ash Clouds
5-21
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |