 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  AVIATION WEATHER
CHAPTER FIVE
41
After Sunrise -
Sun's
Fog May Lift
44
41
39
44
41
Before Noon -
44
Fog Dissipates
Sun's
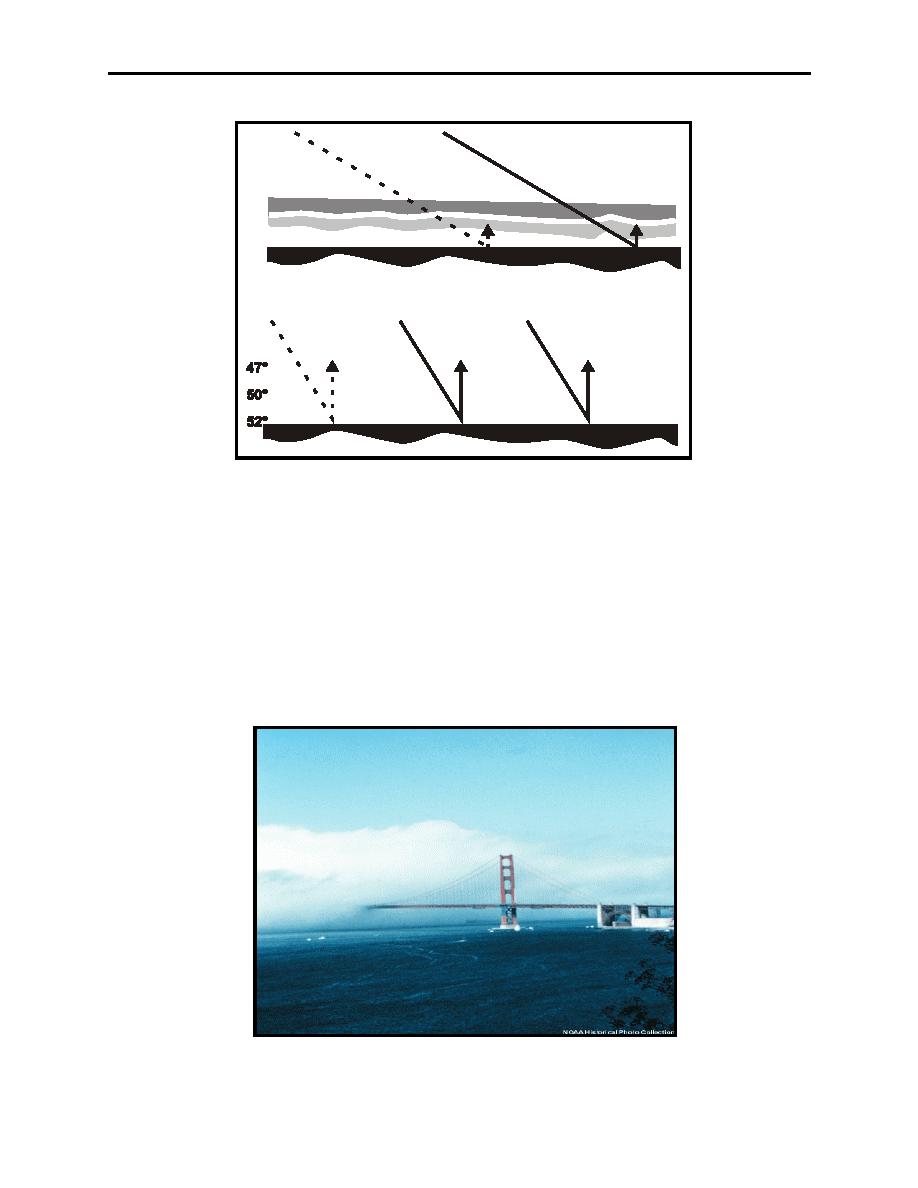
Figure 5-19 Dissipation of Radiation Fog
Advection Fog
Advection fog occurs when warm, moist air moves over a cold surface and the air is cooled to
below its dew point. Common in coastal areas, it is often referred to as sea fog when observed to
come from the sea. Fog of this type becomes thicker and denser as the wind speed increases, up to
about 15 knots. Winds much stronger than this lift the fog into a layer of low stratus. However, in
some oceanic areas, sea fog has been known to persist with winds as high as 40 knots. Advection
fog can stay over the water for weeks, moving over the land late in the day and moving back over
the water the next morning.
Figure 5-20 Advection Fog
Weather Hazards of Turbulence, Icing, Ceilings, Visibility, and Ash Clouds
5-27
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |