 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Transonic and Supersonic Affects on Stability |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  T-45A/C TS, ADV & IUT Aero-02
High-Speed Flight
8.
Increased by transonic and supersonic flight
Sg 1, fr 15
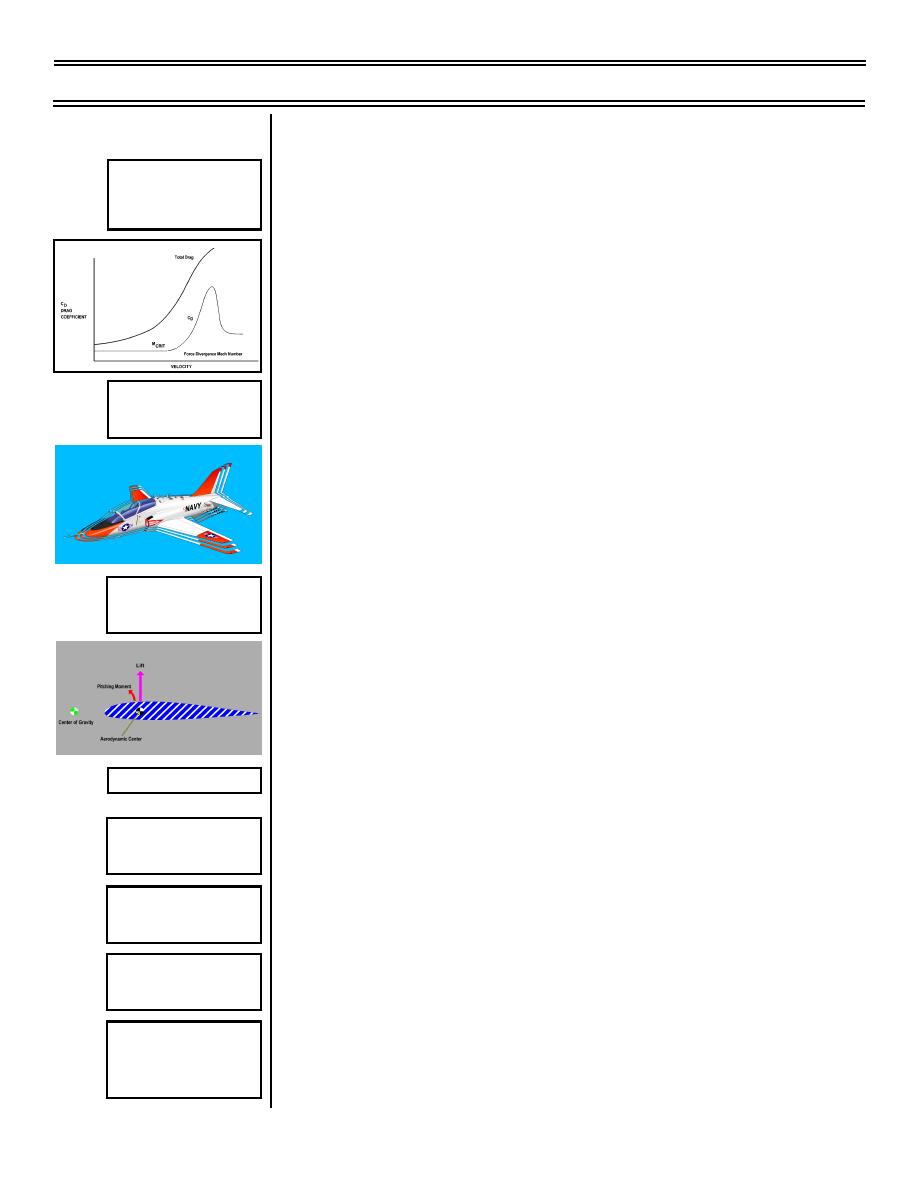
High-Speed Drag
a.
Occurs at the force divergent Mach number and
Characteristics
continues to build
b.
Rate of total aircraft drag rise decreases as the
bow wave attaches
C. Transonic and Supersonic Affects on Stability
1.
Buffeting -- caused by turbulence associated with
Sg 1, fr 16
separation of boundary layers as normal
Airframe Buffeting
compression waves form
2.
Tuck under
a.
Aerodynamic center moves aft, causing a
nose down pitch or "tuck under"
Sg 1, fr 17
Tuck Under
b.
Further increase in flight speed causes a
(1 overlay)
bottom shock
c.
Transonic pitch characteristics
(1) Dive recovery: 0.85-0.90 Mach
(2) Nose-up pitch attributed to an increase in
Overlay 1
the downwash angle at the horizontal tail
Sg 1, fr 18
(3) Increased downwash attributed to spanwise
Fig 3: T-45
lift distribution
Midspan Vortex
(a) Strongest lift gradient normally near
Sg 1, fr 19
wingtip, resulting in wingtip vortexing
Fig 4: Transonic Lift
Distribution
(b) Midspan shock-induced separation
Sg 1, fr 20
results in reduction in lift over outer
Fig 3: T-45
Midspan Vortex
40% of wing, resulting in large lift
gradient at midspan
Sg 1, fr 21
Fig 5: Cause of
(c) Caused by midspan vortex
Reduced T-45 Stability
in Transonic Flight
Page 2-8
(9-99) Original
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |