 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  Stability
T-45A/C TS, E2C2, ADV & IUT Aero-04
H.
Tip Stall
Overlay 2
1.
Stall of the outer portion of wing
2.
May cause loss of ailerons
3.
Cause center of pressure to move forward
Sg 2, fr 10
4.
Aircraft could pitch up if aerodynamic center moves
Leading Edge
forward of the center of gravity
Vortexing
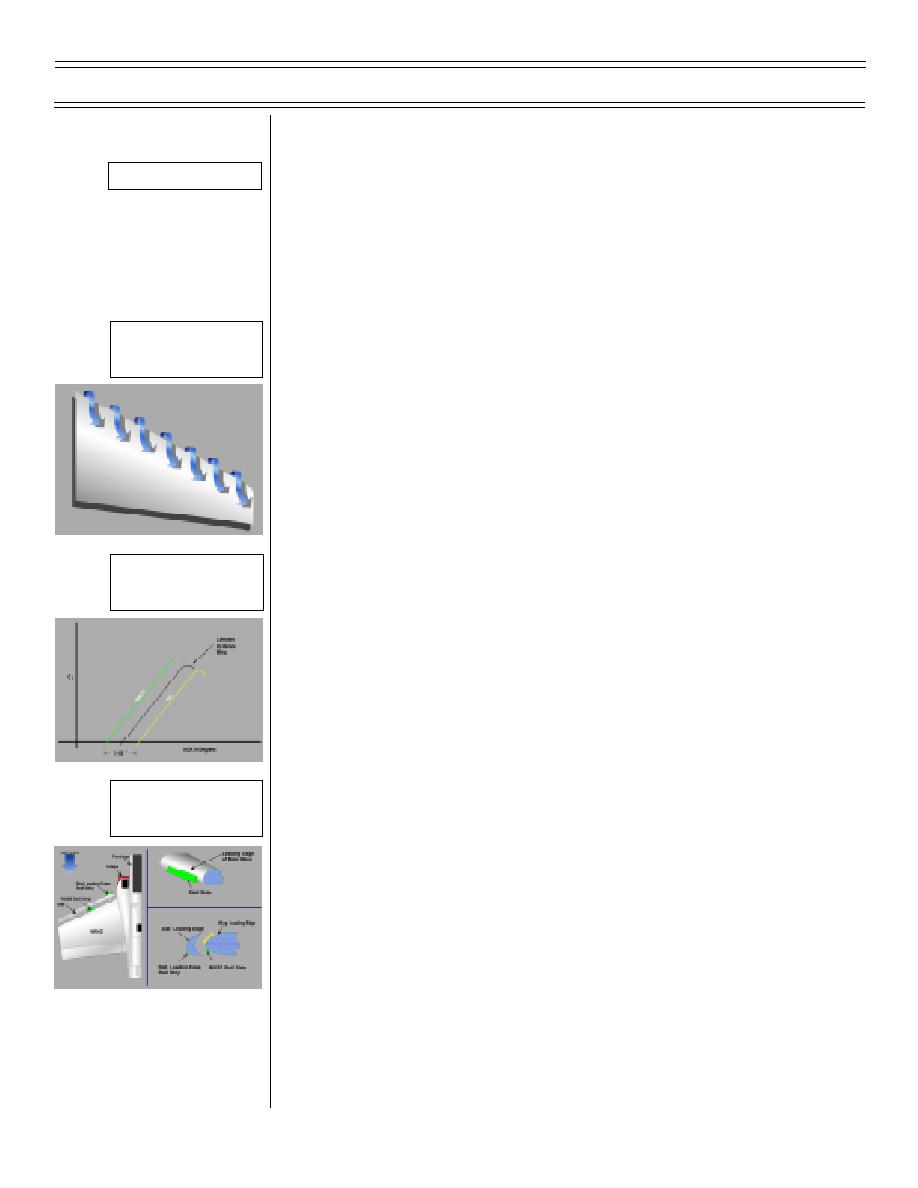
I.
Leading Edge Vortexing
1.
At high angle of attack, high-pressure air from the
bottom of wing jumps past leading edge to lower
pressure area on top of wing
2.
Results in loss of lift and possibly loss of control
Sg 2, fr 11
J.
Geometric Twist
Effect of Geometric
Twist
1.
The wing is designed with a twist that reduces the
angle of incidence at the tip
2.
Wing tip less prone to stall, compared to the root
K.
Stall Strips
1.
Short triangular strips on leading edge of slat and on
wing leading edge, under the slat
Sg 2, fr 12
Stall Strips
2.
Cause root to stall earlier
3.
Works in conjunction with geometric twist to cause
root and tip to stall at about same AOA
L.
Tip versus Root Stall
1.
Undesirable traits of tip stall with a swept wing
design
a.
Little stall warning
b.
Serious reduction in lateral control
Page 4-8
(9-99) Original
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |