 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  INTERMEDIATE FLIGHT PREPARATION WORKBOOK
APPENDIX A
5.
Runway gradient.
6.
Runway surface conditions.
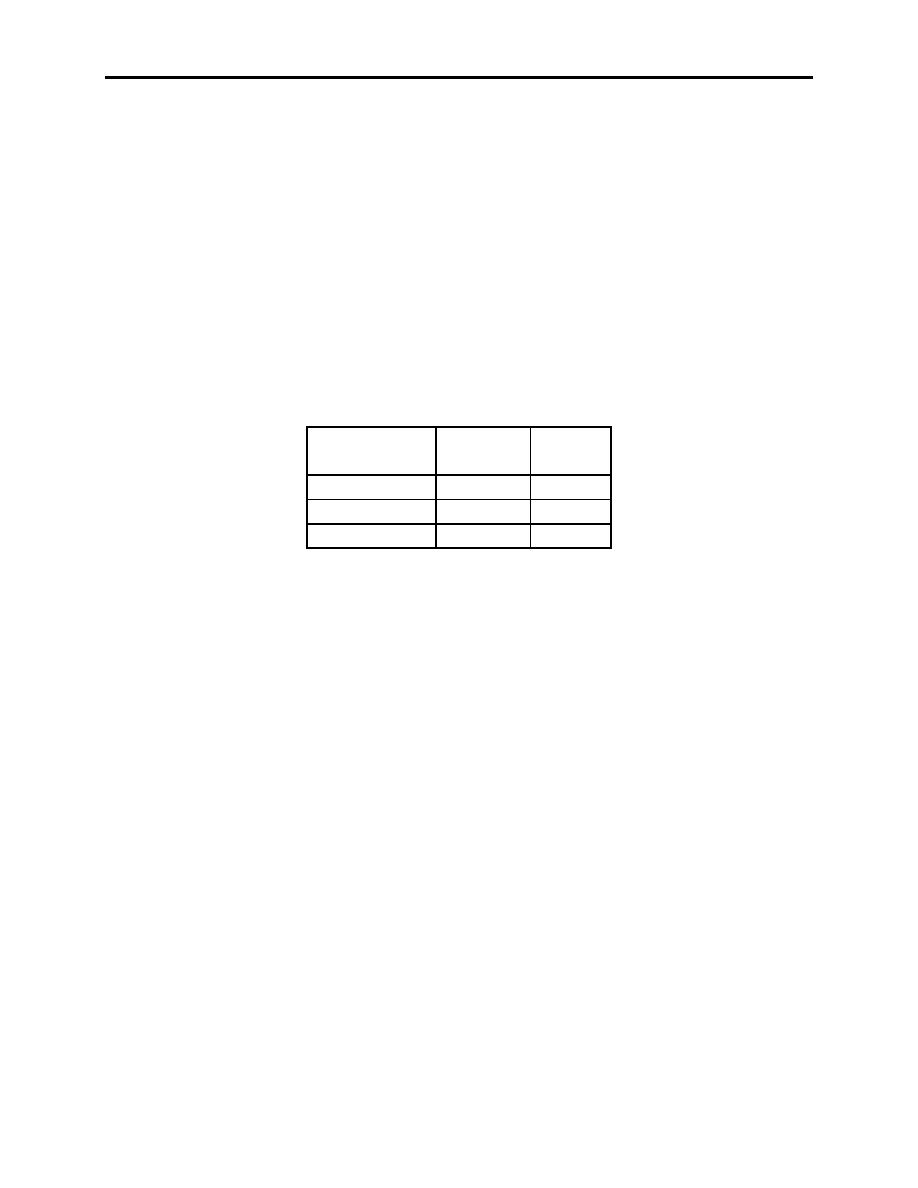
Runway Condition Reading
Runway Condition Reading (RCR) is a measure of tire-to-runway friction coefficient. RCR is
given as a whole number. This value is used to define the braking characteristics for various
runway surface conditions. The reported RCR is therefore a factor in determining any
performance involving braking, such as critical engine failure speed and refusal speed. Some
airfields report runway braking characteristics in accordance with International Civil Aviation
Organization (ICAO) documents, as "good", "medium", and "poor." In order to relate these
ICAO categories to an RCR or when RCR values are not available, the following relationship
will be used:
RUNWAY
ICAO
CONDITION
REPORT
RCR
Dry
Good
23
Wet
Medium
12
Icy
Poor
05
Runway Surface Condition
Runway Surface Condition (RSC) is the average depth covering the runway surface measured to
1/10 inch (1 inch is equivalent to a RSC of 10). RSC types are listed below:
WR
Wet Runway, standing water
SLR
Slush on Runway
LSR
Loose Snow on Runway
PSR
Packed Snow on Runway
IR
Ice on Runway
The RSC affects both the acceleration and stopping performance of the aircraft and must be
accounted for when determining critical field length, critical engine failure speed, and refusal
speed.
Runway Length
Runway length is the paved surface length excluding any overrun.
GLOSSARY
A-3
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |