 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  HELICOPTER AERODYNAMICS WORKBOOK
CHAPTER 5
DYNAMIC ROLLOVER
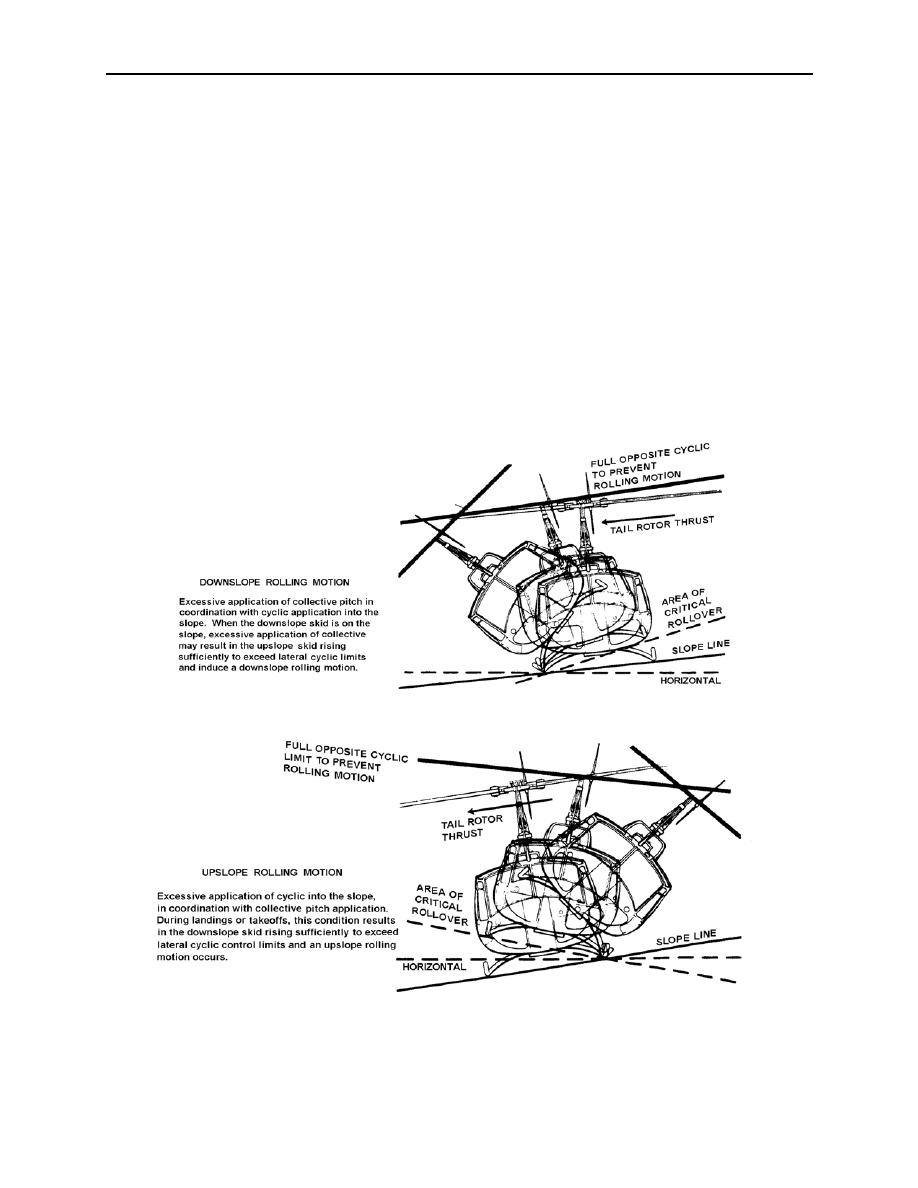
During slope or crosswind landing or takeoff maneuvers, the helicopter is susceptible to a
lateral rolling tendency called dynamic rollover. Each helicopter has a critical rollover angle
beyond which recovery is impossible. If the critical rollover angle is exceeded, the helicopter
will roll over on its side regardless of cyclic input. The rate of rolling motion is also critical. As
the roll rate increases, it reduces the critical rollover angle from which recovery is still possible.
Depending on the helicopter, the critical rollover angle may change, depending on which skid or
wheel is in contact with the ground, the crosswind component, a lateral offset in CG, and amount
of left pedal input for antitorque corrections.
Dynamic rollover begins when the helicopter has only one skid or wheel on the ground and
that gear becomes a pivot point for lateral roll (figure 5-8). When this happens, lateral cyclic
control response is more sluggish and less effective than for a free-hovering helicopter. The gear
may become a pivot point due to an uneven deck surface or poor takeoff/landing technique.
DOWNSLOPE ROLLING MOTION
UPSLOPE ROLLING MOTION
Figure 5-8
FLIGHT PHENOMENA 5-9
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |